Vanguard 500 Index Fund: A Mutual Fund Anyone Can Appreciate In Their 401k
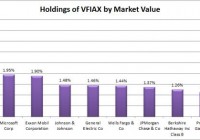
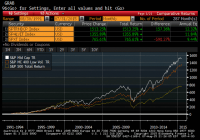
Summary VFIAX is a mutual fund designed to track the S&P 500 with a lower expense ratio than SPY. The mutual fund is a great holding for investors wanting to replicate the performance of “the market” without getting devoured by fees. This is a solid option for the retirement account. The Vanguard 500 Index Fund Admiral Shares (MUTF: VFIAX ) offer investors an excellent way to handle their investments. While I’m a huge fan of using ETFs in the construction of a portfolio, Vanguard is offering some mutual funds with very compelling expense ratios. The nice thing about these mutual funds is that investors are able to buy fractional shares which are excellent for dollar cost averaging. Volatility The standard deviation of returns (monthly) shows very similar levels of volatility to the S&P 500 index as tracked by (NYSEARCA: SPY ). Correlation is also running around 99.9%. The holdings are very similar, but these shares are offering a lower expense ratio and the ability to use dollar cost averaging very effectively. Expense Ratio The mutual fund is posting .05% for an expense ratio. There is really nothing to complain about here. It beats SPY and it beats most mutual funds and ETFs in existence. Largest Holdings The diversification within the fund is good. There are not as many holdings as the whole market index funds that I often prefer, but all around this is a very solid fund. (click to enlarge) Risk Factors The biggest issue for VFIAX is the risk that the S&P 500 is getting fairly expensive on many fundamental levels. For instance, the P/E ratio on the index is fairly high (running over 20). The high P/E ratio comes at a time when corporate profits after taxes are also very high relative to GDP. My concern is about the valuation level of the market. When it comes to ways to buy the market, VFIAX is one of the best funds to use for the task. When it comes to risk assessment, I’m not sure I’d go with Vanguard’s scale, shown below: Vanguard has a tendency to mark any primarily equity investment as being fairly high risk. Relative to other equity investments, the risk level here is very reasonable. The fund still scores high on risk for Vanguard’s scale because they are comparing it to other funds stuffed with lower risk securities than equity. Compared to a very short term high credit quality bond fund, I have to agree that VFIAX has substantially more risk. Compared to the broad universe of equity investments, VFIAX is doing a solid job of holding a diversified portfolio of large capitalization companies with solid histories. Other Things to Know Minimum investments for opening a position were $10,000 according to the Vanguard website. After that additional purchases could be in increments as small as $1. This is a solid fund for dollar cost averaging. Based on my macroeconomic views, I would want to use a fund like VFIAX for equity exposure but I also believing hold some cash on hand is wise given the potential for a reduction in equity prices. When it comes to using mutual funds, I think the best way to deal with them is to dollar cost average in. I like using ETFs to adjust my portfolio exposure but the mutual funds can be set as a “set it and forget it” investment vehicle. When making a meaningful contribution to a fund month after month without checking up on it, it would be wise to make sure the fund is reasonably diversified and that the expense ratios are low. The Vanguard 500 Index Fund Admiral Shares easily sail through both of those tests. Conclusion While I am concerned that market valuations are a little on the high side, I’m still investing each month. I choose to hold more in cash than I would if the market looked cheaper, but I still see dollar cost averaging into the right funds as a viable long term strategy. The biggest challenge for investors is to resist the urge to pull back when the market falls. We should all expect that the stock market will fall within the next 30 years. When those drops happen, investors need to be able to stomach stepping into the market to buy. Since those times are often very scary, one solution is to set up automatic purchases for a fund like VFIAX. To avoid overthinking things, I keep automatic contributions running as a baseline for investing. I use my other accounts to make additional purchases. If your employer sponsored plan offers VFIAX, it is a mutual fund worthy of consideration. Figure out your own risk tolerance and determine if the equity exposure is right for you. The biggest potential mistake an investor could make with buying VFIAX would be to put 75%+ of their portfolio in the fund when they are only a couple years from retirement and will be required to sell off shares to take distributions. So long as the total level of risk is appropriate for the investors, this is a great fund to use as the core of a passive retirement portfolio. Disclosure: I/we have no positions in any stocks mentioned, and no plans to initiate any positions within the next 72 hours. (More…) I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article. Additional disclosure: Information in this article represents the opinion of the analyst. All statements are represented as opinions, rather than facts, and should not be construed as advice to buy or sell a security. Ratings of “outperform” and “underperform” reflect the analyst’s estimation of a divergence between the market value for a security and the price that would be appropriate given the potential for risks and returns relative to other securities. The analyst does not know your particular objectives for returns or constraints upon investing. All investors are encouraged to do their own research before making any investment decision. Information is regularly obtained from Yahoo Finance, Google Finance, and SEC Database. If Yahoo, Google, or the SEC database contained faulty or old information it could be incorporated into my analysis.